Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat accumulates in liver cells, leading to conditions like NAFLD (non-alcoholic) and alcoholic fatty liver․ Diet and lifestyle changes are crucial for reversal․
1․1 What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat builds up in liver cells, leading to conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease․ NAFLD is not caused by alcohol but is linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome․ If left untreated, it can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, or even liver failure․ Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by heavy alcohol consumption․ Both types require lifestyle changes, with diet playing a central role in managing and reversing early stages․ A healthy diet helps reduce liver fat, inflammation, and the risk of complications, making it essential for overall liver health and well-being․
1․2 Types of Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD and Alcoholic Fatty Liver)
Fatty liver disease is primarily categorized into two types: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; NAFLD occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver due to factors like obesity, insulin resistance, or metabolic syndrome, unrelated to alcohol consumption․ It can progress to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, or liver failure․ Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease results from heavy alcohol use, leading to fat buildup and inflammation․ Both types require attention to diet and lifestyle to manage symptoms and prevent progression․ Understanding the distinction is crucial for tailored treatment approaches․
1․3 Importance of Diet in Managing Fatty Liver
Diet plays a critical role in managing fatty liver disease, as it directly impacts liver fat accumulation and inflammation․ A well-structured diet helps reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and prevent disease progression․ Foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados and olive oil, support liver function, while avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks reduces fat buildup․ The Mediterranean diet, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, is often recommended․ Weight loss through dietary changes can reverse early stages of fatty liver disease․ A balanced and nutrient-rich diet is essential for maintaining liver health and overall well-being․

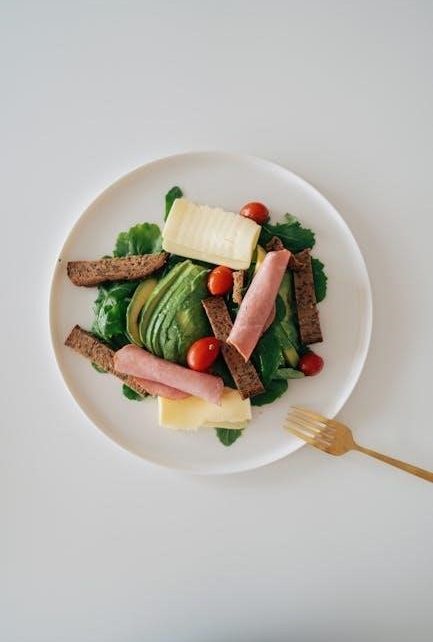
Key Components of a Fatty Liver Diet Plan
A fatty liver diet focuses on healthy fats, lean proteins, and high fiber to reduce liver fat; Avoid processed foods, sugars, and alcohol to support liver health and weight management․
2․1 Healthy Fats: Avocados, Olive Oil, and Nuts
Healthy fats are essential for a fatty liver diet, as they support liver function and reduce inflammation․ Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats, which improve cholesterol levels and provide sustained energy․ Olive oil, another monounsaturated fat, is anti-inflammatory and supports liver detoxification․ Nuts like almonds and walnuts offer omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce liver fat and inflammation․ These fats should be consumed in moderation due to their calorie density․ Incorporating them into meals like salads, smoothies, or as cooking oils can enhance the effectiveness of your fatty liver diet plan․ Always choose unprocessed forms to maximize benefits․
2․2 Foods to Avoid: Processed Foods, Sugary Drinks, and Refined Carbs
Processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbs are detrimental to liver health and should be avoided in a fatty liver diet․ These foods are high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and empty calories, which promote fat accumulation in the liver․ Refined carbs, such as white bread and pasta, cause rapid insulin spikes, contributing to liver fat storage․ Sugary drinks like soda and sweetened beverages increase calorie intake without nutritional value, worsening fatty liver․ Processed foods often contain harmful additives and preservatives that further strain liver function․ Eliminating these from your diet can significantly reduce liver fat and improve overall health․ Opt for whole, nutrient-dense foods instead․
2․3 The Role of Protein in Liver Health
Protein plays a vital role in supporting liver health, particularly for individuals with fatty liver disease․ It aids in repairing liver cells and maintaining metabolic functions․ Lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, and plant-based options like beans and tofu, are ideal․ These proteins help reduce liver inflammation and promote fat metabolism․ Avoiding excessive intake of saturated fats and focusing on high-quality proteins can improve liver function․ Incorporating protein-rich foods into meals helps stabilize blood sugar levels and prevents excessive fat storage in the liver․ A balanced intake of protein is essential for overall liver health and supports weight management, which is critical for reversing fatty liver disease․
2․4 Importance of Fiber and Vegetables
Fiber and vegetables are essential for managing fatty liver disease․ Fiber aids digestion, reduces fat accumulation in the liver, and helps regulate blood sugar levels․ Vegetables, particularly non-starchy options like spinach, broccoli, and carrots, are rich in antioxidants and vitamins that support liver detoxification․ A diet high in fiber can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing liver inflammation․ Incorporating a variety of colorful vegetables ensures a broad intake of nutrients, which are crucial for overall health and liver function․ A balanced diet rich in fiber and vegetables not only supports weight management but also promotes the reversal of fatty liver disease by enhancing metabolic processes and reducing liver fat․

The Mediterranean Diet for Fatty Liver
The Mediterranean Diet emphasizes healthy fats, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, supporting liver health by reducing inflammation and fat accumulation, with antioxidants and Omega-3s promoting liver function․
3․1 Overview of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is a well-rounded eating pattern rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like olive oil․ It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods and limits refined carbs and sugary products․ This diet is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and is often recommended for improving liver health․ By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, it helps reduce liver fat and promotes overall well-being․ The Mediterranean Diet is not just a diet but a sustainable lifestyle choice that supports long-term health benefits, making it an excellent option for managing fatty liver disease effectively․
3․2 Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet for Liver Health
The Mediterranean Diet offers significant benefits for liver health by reducing liver fat and inflammation․ Its focus on healthy fats, such as olive oil, and antioxidants helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower triglycerides․ The diet’s anti-inflammatory properties can prevent liver damage and progression of fatty liver disease․ Additionally, it promotes weight management, which is crucial for reducing liver fat accumulation․ By emphasizing whole, nutrient-rich foods, the Mediterranean Diet supports overall liver function and reduces the risk of complications associated with fatty liver disease, making it a highly recommended choice for those seeking to improve their liver health․
3․3 Incorporating Mediterranean Diet Principles into Your Meal Plan
Incorporate Mediterranean Diet principles by focusing on healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, and nuts․ Prioritize whole grains, lean proteins, and a variety of colorful vegetables․ Limit refined carbs and processed foods․ Include fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, at least twice a week․ Use herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt and sugar․ Aim for 5-7 servings of fruits and vegetables daily․ Stay hydrated with water or herbal teas․ For snacks, opt for nuts, seeds, or fresh fruit․ Plan balanced meals with a protein source, whole grains, and a side of steamed or roasted vegetables to support liver health and overall well-being․
7-Day Fatty Liver Diet Meal Plan Sample
A 7-day meal plan for fatty liver includes healthy fats, lean proteins, and fiber-rich foods to promote weight loss and liver health․
4․1 Breakfast Ideas: Healthy Options to Start Your Day
Starting your day with a nutrient-rich breakfast is essential for managing fatty liver․ Consider options like oatmeal with berries, avocado toast on whole-grain bread, or a smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk․ Eggs are also a great choice, whether scrambled with vegetables or made into an omelette․ Incorporate healthy fats like chia seeds or flaxseeds for added fiber and omega-3s; Avoid sugary cereals and opt for whole grains instead․ A balanced breakfast helps stabilize blood sugar and provides energy, supporting liver health and weight management․ Aim for variety to keep your meals engaging and ensure you’re getting a mix of vitamins and minerals․
4․2 Lunch and Dinner Recipes: Balanced and Nutritious Meals
For lunch and dinner, focus on balanced meals rich in lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber․ Grilled chicken or fish with roasted vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts is an excellent choice․ Quinoa or brown rice bowls with avocado, beans, and mixed greens are also nutritious options․ Consider recipes like baked salmon with asparagus or turkey lettuce wraps with olive oil dressing․ These meals provide sustained energy and support liver health by reducing inflammation and fat accumulation․ Avoid processed meats and opt for herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt or sugar․ Portion control is key to maintaining a healthy weight and liver function․
4․3 Snacks and Desserts: Healthy Alternatives
Healthy snacks and desserts are essential for maintaining energy and satisfaction without harming liver health․ Opt for fresh fruits like berries or apples, paired with a handful of nuts or seeds for healthy fats and fiber․ Veggie sticks with hummus or guacamole make great snack options․ For desserts, consider Greek yogurt with berries, dark chocolate (70% cocoa or higher), or fruit salads․ Avoid sugary treats and refined carbs․ Air-popped popcorn without added butter or salt is another nutritious choice․ These alternatives support liver health by reducing inflammation and promoting a balanced diet․ Portion control is key to maintaining a healthy weight and liver function․

Lifestyle Changes to Support Liver Health
Regular physical activity, stress management, and sufficient sleep are vital for liver health․ These changes complement dietary adjustments, promoting overall well-being and fatty liver reversal․
5․1 Exercise: The Role of Physical Activity in Reducing Liver Fat
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in reducing liver fat and improving overall health․ Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week․ Exercise helps burn calories, reduce body fat, and improve insulin sensitivity, all of which are essential for managing fatty liver disease․ Strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can also be beneficial․ Even small amounts of physical activity can make a significant difference in liver health and support weight loss, a key factor in reversing fatty liver disease․
5․2 Weight Loss: How to Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Weight
Weight loss is a cornerstone of managing fatty liver disease, as excess body fat contributes to liver fat accumulation․ Aim for a gradual weight loss of 0․5–1 kg per week through a calorie-controlled diet․ A daily calorie deficit of 500 calories is often recommended․ Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes․ Combining a healthy diet with regular physical activity helps maintain weight loss over time․ Monitoring food intake and staying hydrated are key․ Professional guidance from a dietitian can also provide personalized strategies for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, which is essential for reducing liver fat and improving overall health․
5․3 Managing Stress and Sleep for Overall Health
Managing stress and ensuring adequate sleep are vital for overall health, particularly when addressing fatty liver disease․ Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, potentially leading to fat accumulation in the liver․ Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt hormones that regulate hunger and metabolism, making weight management more challenging․ Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into your daily routine․ Aim for 7–9 hours of high-quality sleep each night by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime environment․ Addressing these factors supports liver health and complements dietary and lifestyle changes aimed at reducing liver fat and improving overall well-being․

Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Diet
Regular check-ups and blood tests help track liver health improvements․ Adjust your diet based on progress, ensuring weight loss and reduced liver fat․ Consult your healthcare provider for personalized tweaks to maintain optimal results․
6․1 How to Track Liver Health Improvements
Monitoring liver health involves regular blood tests to measure liver enzymes and inflammation levels․ Imaging techniques like ultrasound can also assess liver fat reduction․ Track weight loss, as a 7-10% reduction often improves fatty liver․ Keep a food diary to ensure diet adherence and note physical changes, such as increased energy or reduced bloating․ Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to evaluate progress and adjust your plan․ Consistent monitoring helps identify improvements and ensures long-term liver health benefits, guiding necessary adjustments to your fatty liver diet plan․
6․2 Adjusting Your Diet Based on Progress and Needs
As you progress with your fatty liver diet plan, it’s important to reassess and adjust your diet based on individual needs and improvements․ If weight loss occurs, incorporate more protein-rich foods to maintain muscle mass․ Increase fiber intake if bloating or digestive issues persist․ Consult with a healthcare provider or dietitian to tailor your meal plan further․ Regularly review food diaries to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments․ Stay updated on the latest research and incorporate new recommendations to optimize liver health․ Personalized dietary changes ensure sustained progress and long-term success in managing fatty liver disease․

Resources for a Fatty Liver Diet Plan
Access detailed guides, meal plans, and expert recommendations in a fatty liver diet plan PDF․ Explore trusted websites like Harvard Medical School and Mayo Clinic for additional resources․
7․1 Where to Find a Fatty Liver Diet Plan PDF
A fatty liver diet plan PDF can be found on reputable health websites, medical institutions, and dietary resource platforms․ Websites like Harvard Medical School, Mayo Clinic, and Web MD often provide comprehensive guides․ Additionally, platforms like Google Scholar and health-focused forums offer downloadable resources․ Ensure the source is credible and medically endorsed for accuracy․ Use keywords like “fatty liver diet plan PDF” or “NAFLD meal plan download” to locate reliable files․ Many healthcare providers also offer free PDF guides as part of patient resources․ Always verify the credibility of the source to ensure the information is safe and effective for managing fatty liver disease․
7․2 Recommended Books and Websites for Fatty Liver Diet Information
For reliable fatty liver diet information, consider consulting books like “The Fatty Liver Diet Guide” by Dr․ Sandra Cabot or “The Mediterranean Diet” by Dr․ Catherine Itsiopoulos․ Websites such as Healthline, Mayo Clinic, and Mediterranean Living offer evidence-based resources․ Platforms like PubMed and Google Scholar provide access to scientific studies and expert recommendations․ Additionally, health-focused forums and support groups often share practical advice and meal plans․ Always choose sources backed by medical professionals to ensure accuracy and safety․ These resources can complement your diet plan PDF, offering a well-rounded approach to managing fatty liver disease effectively․
Adopting a fatty liver diet plan, along with lifestyle changes, can significantly improve liver health․ Start your journey with a structured plan and professional guidance for lasting results․
8․1 Summary of Key Points
A fatty liver diet plan focuses on reducing liver fat through dietary and lifestyle changes․ Key components include consuming healthy fats, avoiding processed foods, and incorporating the Mediterranean diet․ Regular exercise, weight loss, and avoiding alcohol are crucial for improving liver health; Monitoring progress and adjusting the diet plan based on individual needs is essential․ A structured 7-day meal plan can provide guidance, ensuring balanced nutrition․ Consistency and professional advice are vital for long-term success․ By adhering to these principles, individuals can effectively manage fatty liver disease and promote overall well-being․
- Emphasize healthy fats and fiber-rich foods․
- Limit sugary drinks and refined carbs․
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight․
- Consider a Mediterranean diet approach․
- Monitor liver health and adjust the diet plan as needed․
8․2 Encouragement to Start Your Fatty Liver Diet Journey

Starting your fatty liver diet journey may seem challenging, but it is a vital step toward improving your liver health and overall well-being․ Small, consistent changes can lead to significant results, such as reduced liver fat and inflammation․ Remember, this is a journey, not a quick fix․ Every healthy choice brings you closer to a healthier liver and a better quality of life․ Don’t hesitate to seek support from healthcare professionals or online resources like the fatty liver diet plan PDF․ Take the first step today, and celebrate the progress you make along the way․ Your liver—and your body—will thank you․



